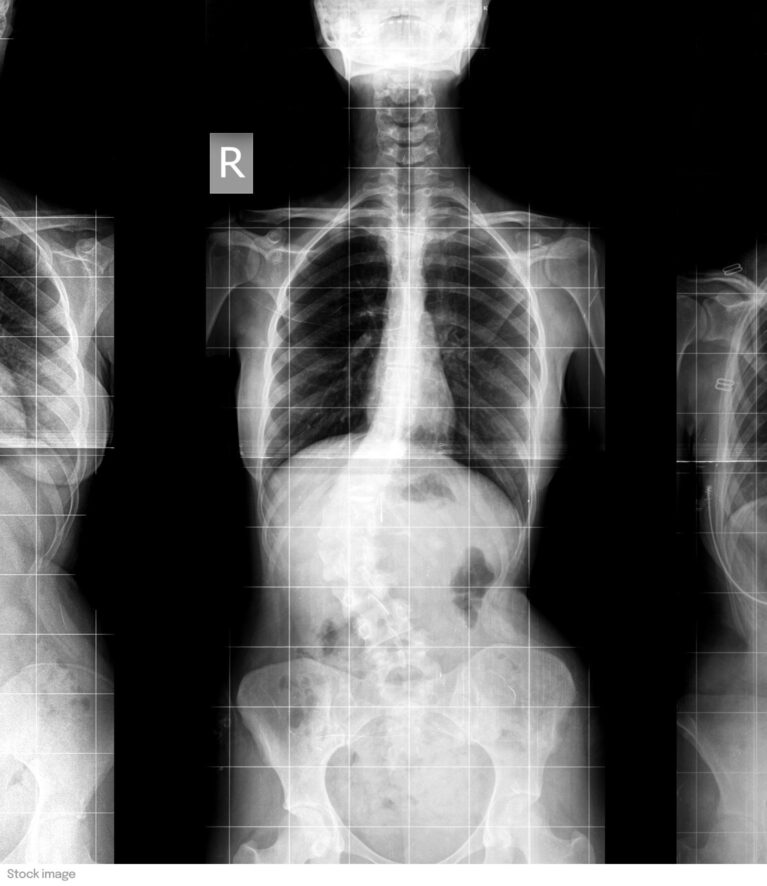
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a permanent deformity of the spine in all three planes due to rotation of the vertebrae in relation to each other.
There are several types of scoliosis. Idiopathic scoliosis in children and adolescents has no known cause. Secondary scoliosis is the result of neuromuscular or bone disease. Finally, adult scoliosis, or degenerative scoliosis, is related to degeneration of the intervertebral discs and vertebrae. The diagnosis is made by clinical examination and medical imaging.
The consequences of severe scoliosis are a reduction in breathing capacity, back pain and a change in the aesthetic aspect.
The main aim of treatment is to prevent the spinal deformity from getting worse. Physiotherapy, followed by orthopaedic treatment with corsets, is an option often chosen when scoliosis is progressive. If there is no response to the previous treatments, surgery is planned. This is an arthrodesis of the spine that corrects the curves and fixes the vertebrae with screws, hooks, rods and bone grafts to achieve vertebral fusion.