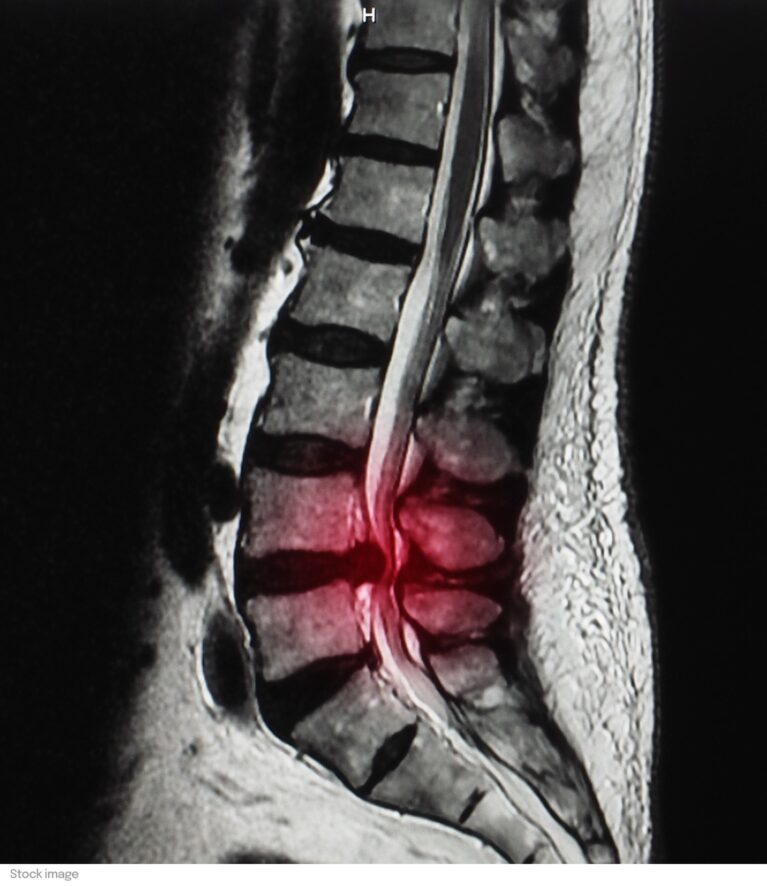
Herniated disc
A herniated disc is a pathology of the spinal column, in particular of the intervertebral disc. The destruction of the fibrous ring causes part or all of the nucleus pulposus to flow into the spinal canal. The resulting protrusion of the disc leads to stenosis of the spinal canal.
Symptoms depend on the disc affected and its location, although the majority of herniated discs are in the lumbar region; from asymptomatic, the herniation may also cause back pain, neurological pain due to compressed nerves, or muscle weakness, numbness or tingling.
The usual treatment is medical, with prescription painkillers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Corticosteroid infiltrations are also suggested, but their duration and effectiveness are variable. Finally, if there is no response to the previous treatments or if there is a significant neurological deficit, surgery is proposed to the patient. In this case, the aim is to reduce or eliminate the compression of the intervertebral disc in order to relieve the pain, restore the nerves and restore sensory and motor functions.